Page 75 - EXIM-BANK-AR20
P. 75
Section 05 Upholding Accountability
73
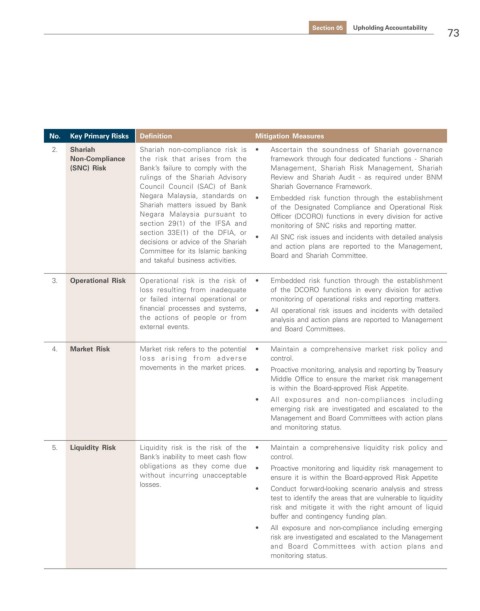
No. Key Primary Risks Definition Mitigation Measures
2. Shariah Shariah non-compliance risk is • Ascertain the soundness of Shariah governance
Non-Compliance the risk that arises from the framework through four dedicated functions - Shariah
(SNC) Risk Bank’s failure to comply with the Management, Shariah Risk Management, Shariah
rulings of the Shariah Advisory Review and Shariah Audit - as required under BNM
Council Council (SAC) of Bank Shariah Governance Framework.
Negara Malaysia, standards on • Embedded risk function through the establishment
Shariah matters issued by Bank of the Designated Compliance and Operational Risk
Negara Malaysia pursuant to Officer (DCORO) functions in every division for active
section 29(1) of the IFSA and monitoring of SNC risks and reporting matter.
section 33E(1) of the DFIA, or • All SNC risk issues and incidents with detailed analysis
decisions or advice of the Shariah and action plans are reported to the Management,
Committee for its Islamic banking Board and Shariah Committee.
and takaful business activities.
3. Operational Risk Operational risk is the risk of • Embedded risk function through the establishment
loss resulting from inadequate of the DCORO functions in every division for active
or failed internal operational or monitoring of operational risks and reporting matters.
financial processes and systems, • All operational risk issues and incidents with detailed
the actions of people or from analysis and action plans are reported to Management
external events. and Board Committees.
4. Market Risk Market risk refers to the potential • Maintain a comprehensive market risk policy and
loss arising from adverse control.
movements in the market prices. • Proactive monitoring, analysis and reporting by Treasury
Middle Office to ensure the market risk management
is within the Board-approved Risk Appetite.
• All exposures and non-compliances including
emerging risk are investigated and escalated to the
Management and Board Committees with action plans
and monitoring status.
5. Liquidity Risk Liquidity risk is the risk of the • Maintain a comprehensive liquidity risk policy and
Bank’s inability to meet cash flow control.
obligations as they come due • Proactive monitoring and liquidity risk management to
without incurring unacceptable ensure it is within the Board-approved Risk Appetite
losses.
• Conduct forward-looking scenario analysis and stress
test to identify the areas that are vulnerable to liquidity
risk and mitigate it with the right amount of liquid
buffer and contingency funding plan.
• All exposure and non-compliance including emerging
risk are investigated and escalated to the Management
and Board Committees with action plans and
monitoring status.